Calcium is a mineral everyone is aware of. While the dairy industry has claimed it as their own – or they’ve proclaimed themselves as its top source – calcium, like all other minerals, comes from the soil. This means, we can get it through plants just like any other mineral.
Plant-based doctors often say we should skip the middle animal (cows) and get it straight from greens just like they do. This is true, if we eat our dark leafy greens every day, we can get all the calcium we need. Except for spinach, beet greens, and chard which are high in oxalates that bind to calcium. Other great sources include white beans, soybeans, chia seeds, sesame seeds, and almonds!
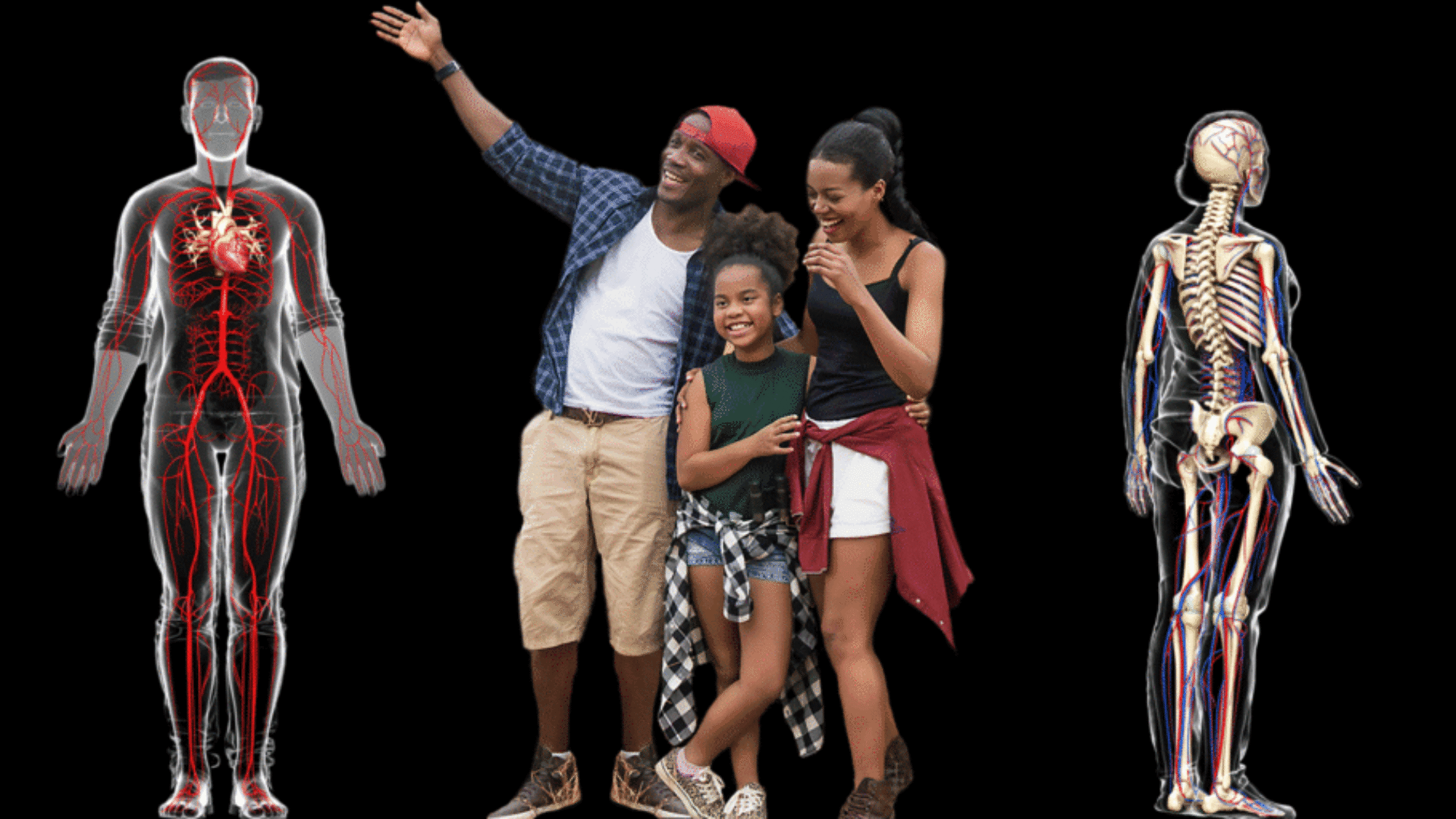
While most of us know that calcium is crucial for our bones, it’s also important for our heart, our brain cells or neurons, our muscles, and our blood.
Calcium Absorption and Intake Recommendations
Worried about not reaching the U.S. intake recommendations with plant-based sources? Here’s something we all need to understand. These recommendations are based on dairy absorption rates. We only absorb from 30 to 35% of calcium from dairy. If we ingest 1300 mg (U.S. Daily Value), we are only absorbing about 390 mg. If we instead get it from low-oxalate dark leafy greens, we’ll absorb 50-60%. So, to reach the same 390 mg, we only need to ingest 750 mg of calcium.
Most people need less, though, because their Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) is typically less than the Daily Value (DV). This is probably why nutrition sites like NutritionFacts.org or the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine recommend a daily intake of at least 600 mg. Now, that’s a lot easier to reach through a balanced, whole-food, plant-based diet!
On this page, we’ll share the best foods to help you reach your intake needs, a nutrition calculator to help you identify your RDA as well as your family’s, further details on what this mineral can do for us, some important facts, and a comparison between whole-food, plant-based sources, supplements, and animal-based sources. Enjoy!
Top Whole-Food, Plant-Based Sources
Hover over each food below to see how much calcium you can get with one serving. Click on each food’s picture to visit its interactive page with a personalized calculator of all the nutrition you can get from one serving, more information about how it supports our body, tips to choose and prepare it, interesting facts, and more!
Calcium Personalized Calculator
See how much calcium you and your family members need, according to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025. As a reminder, plant-based sites NutritionFacts.org and the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine recommend a daily intake of at least 600 mg a day from dark leafy greens due to the higher amount of calcium we can absorb from this source, compared to only 30-35% from dairy.
Terminology:
- Daily Value (DV): The recommended amount of nutrients to consume each day for individuals who are 4 years old or older.
- Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA): The recommended amount of nutrients to consume each day according to the individual’s age, gender, and whether a woman is pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Upper Intake Level (UL): The highest amount of nutrient intake that will not pose adverse health effects on most individuals.
How Our Body Uses Calcium
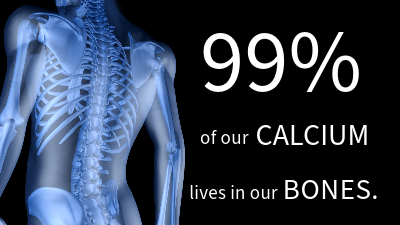
99% of the calcium in our body is stored in our bones and teeth, but other parts of our body also need this nutrient for proper functioning. Hover over each pointer below for more details on how our body uses calcium. Click on the pointer to visit the specific body part’s interactive page to discover what other nutrients support it, the best sources to find them, and other interesting facts.
Important Things to Know
Comparison of Calcium Sources
You may be wondering about other potential sources of this nutrient, such as supplements and dairy. Below we make a quick and simple comparison between the three choices, including absorption rates for each and the risks found in non plant-based options.
References