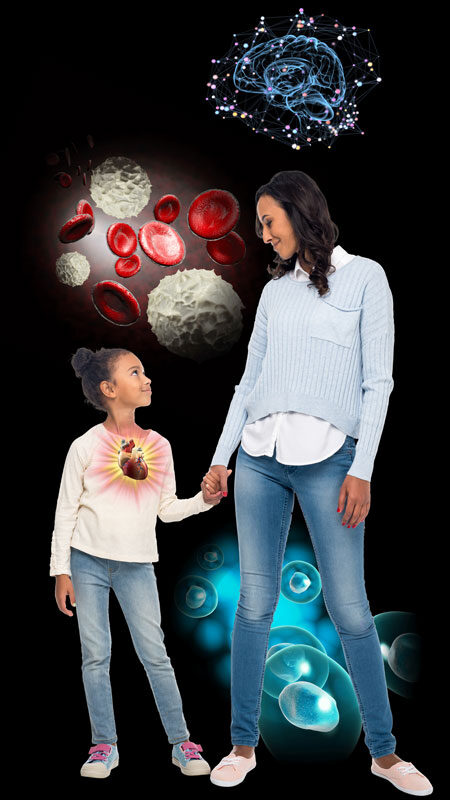
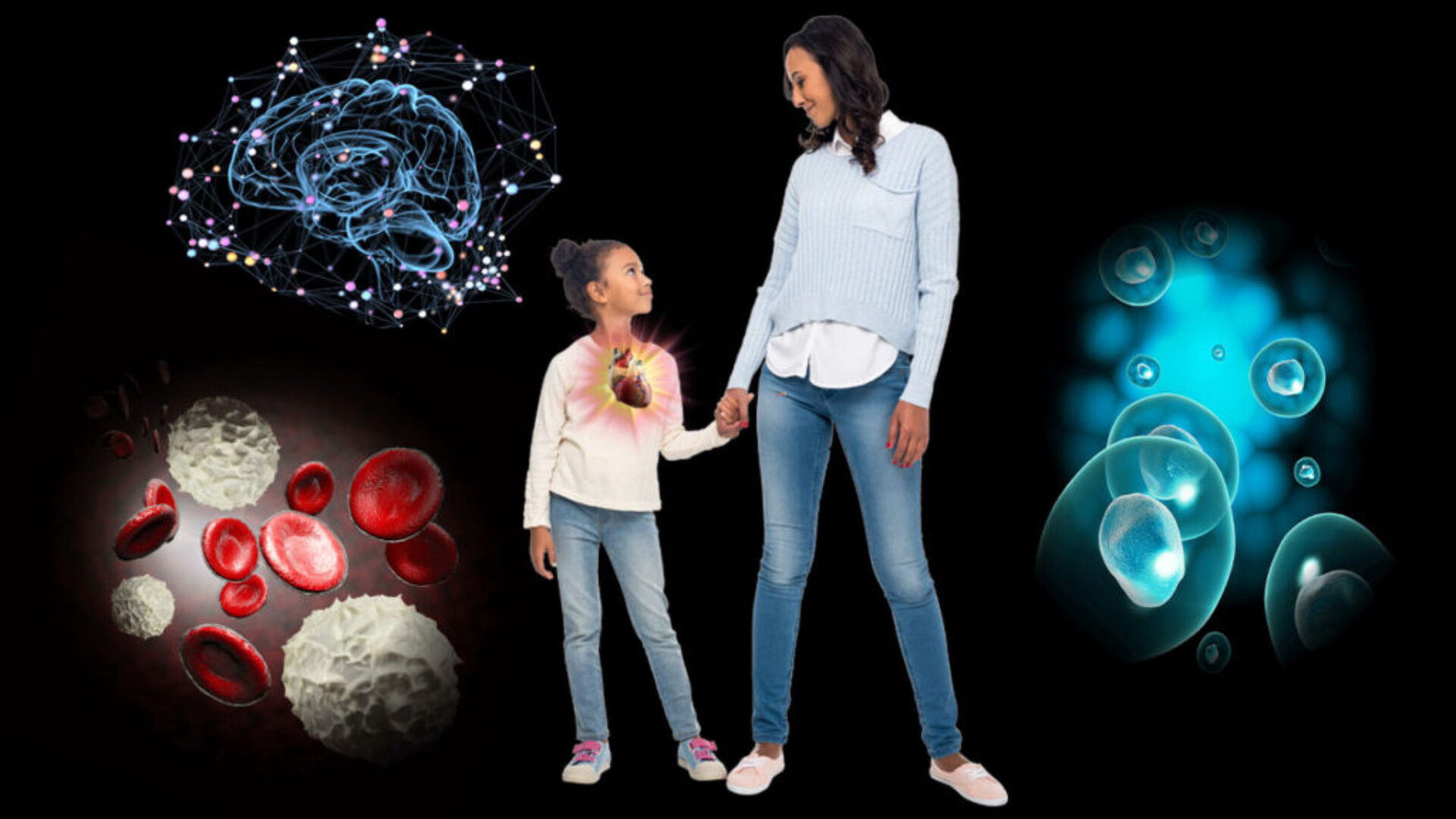
Vitamin E is a strong, fat-soluble antioxidant that can really make a difference to our heart, our immune system, our brain, our muscles, and our cells. We can find it in sunflower seeds, almonds, leafy greens, and in some vegetables and fruits. Yet, 93% of Americans aren’t getting enough. This is likely because they’re not getting enough whole, plant-based foods in their diet. Animal-based foods are not a good source of this nutrient.
Getting this vitamin from supplements is not our best choice. Taken in high amounts can lead to toxicity which could result in hemorrhage, or even a stroke. But even if we stay under the Tolerable Upper Intake limits, vitamin E supplements are associated with a higher risk of developing prostate cancer.
Our best choice is to get it from some of its multiple plant-based sources. We can never get too much of this vitamin from plants, but to absorb it, we do need to follow a balanced diet that includes some healthy fatty foods. In fact, some of its top sources are healthy fatty foods!
Below, you will learn more about what this important nutrient does for our body, its top sources, and some interesting facts. Plus, you can use our personalized nutrition calculator to determine how much you and your family need.
Top Whole-Food, Plant-Based Sources of Vitamin E
The top source are sunflower seeds, followed closely by almonds. But there are many other delicious sources that provide us with a good amount. Hover over each food below to see how much of the Daily Value (DV) of vitamin E you can get with one serving. Click on each food’s picture to visit its interactive page.
Vitamin E Personalized Calculator
See how much vitamin E you and your family members need, according to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025. Getting your personalized nutrition values will give you a better idea of how to plan your meals and family portions.
Terminology:
- Daily Value (DV): The recommended amount of nutrients to consume each day for individuals who are 4 years old or older.
- Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA): The recommended amount of nutrients to consume each day according to the individual’s age, gender, and whether a woman is pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Upper Intake Level (UL): The highest amount of nutrient intake that will not pose adverse health effects on most individuals.
How Our Body Uses Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a key nutrient for our heart, our brain, our muscles, our immunity, and our cells. Hover over each pointer below for more details on how this vitamin aids our body. Click on the pointer to visit the specific body part’s interactive page to discover what other nutrients support it, the best sources to find them, and other interesting facts.
Important Things to Know About Vitamin E
Vitamin E Sources Comparison
You may be wondering about other potential sources of vitamin E aside from delicious seeds, nuts, vegetables and fruits. Though, why would you? In case you do, check out our quick comparison between whole plants, supplements, and animal-based products. For vitamin E the top choice is clear!