Vitamin B2 or riboflavin is a water-soluble vitamin that we need to replenish regularly since we can’t store it in our body. It is a key nutrient for our reproduction and to support early development. Therefore, it’s important to make sure we’re getting enough if we’re planning to get pregnant, during the pregnancy, and during lactation. Our babies need riboflavin for the development of their gastrointestinal tract after birth.
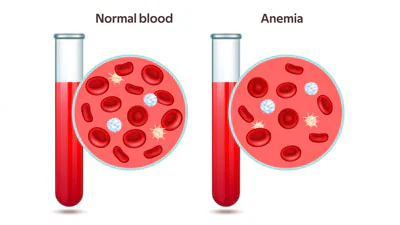
Other important functions of vitamin B2 include the breakdown of proteins, carbohydrates and fats into energy. Riboflavin also helps with red blood cell production and the transportation of oxygen to our cells, and may help prevent anemia. As an antioxidant, it helps our immune system. Plus, this vitamin might also help prevent thyroid disease, cataracts, and migraines. It even helps us have healthy hair and skin!
Deficiency is extremely rare, but women who have been on the birth control pill are at a higher risk. Also, if they are pregnant or lactating, older people, those with an alcohol dependency, and vegans who do not follow a proper, balanced diet. Some deficiency symptoms include cataracts, anemia and, during pregnancy, it may increase the risk of preeclampsia and birth defects.
Try our personalized calculator below to see how much vitamin B2 or riboflavin you and your loved ones need. Also, discover some of the top whole-food, plant-based sources, learn some interesting facts about riboflavin, and check out our nutrient source comparison.
Top Whole-Food, Plant-Based Sources
Hover over each food below to see how much riboflavin or vitamin B2 you can get with one serving. Click on each food’s picture to visit its interactive page with a personalized calculator of all the nutrition you can get from one serving, more information about how it supports our body, tips to choose and prepare it, interesting facts, and more!
Vitamin B2 Personalized Calculator
See how much riboflavin or vitamin B2 you and your family members need, according to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025.
Terminology:
- Daily Value (DV): The recommended amount of nutrients to consume each day for individuals who are 4 years old or older.
- Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA): The recommended amount of nutrients to consume each day according to the individual’s age, gender, and whether a woman is pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Upper Intake Level (UL): The highest amount of nutrient intake that will not pose adverse health effects on most individuals.
Important Things to Know
Comparison of Vitamin B2 Riboflavin Sources
You may be wondering about other potential sources of riboflavin, such as supplements and meat. Below we make a quick and simple comparison between the three choices.
References